Bringing a tiny human into the world is an exciting experience for many families. It can be a fun—yet tiresome—experience for mothers as their bodies are stretched to their limits. During those 9 (or fewer) months, they endure more aches and pains than ever before, and begin to crave… interesting… food combos. (Pickles and ice cream, anyone??)
Pregnancy experiences for ADHDers may have different challenges compared to average neurotypical pregnancies. This isn’t to say that ADHDers who desire to conceive will undoubtedly have a completely stressful pregnancy—they just need a plan to manage their symptoms in the safest way.
So, how does ADHD affect pregnancy—and vice versa? What about ADHD medications? Do they have effects on expecting mothers and their womb nuggets?
Let’s dive in!
Too long; didn’t read
- More research is needed to understand (1) how pregnancy and ADHD affect one another, and (2) how ADHD medication affects pregnant people and their unborn child.
- Pregnancy and birth complications have been documented in women with ADHD. This risk increases when the mother is taking stimulant medication.
- Most people produce estrogen throughout their life because it functions as a regulator for several biological processes3
- Estrogen affects dopamine production and transportation5, which is why pregnancy can improve ADHD symptoms.
- Non-medication alternatives for ADHD treatment include CBT, ADHD management apps, and lifestyle adjustments.
What is ADHD?
ADHD, or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, is a neurodevelopmental condition that affects both children and adults.
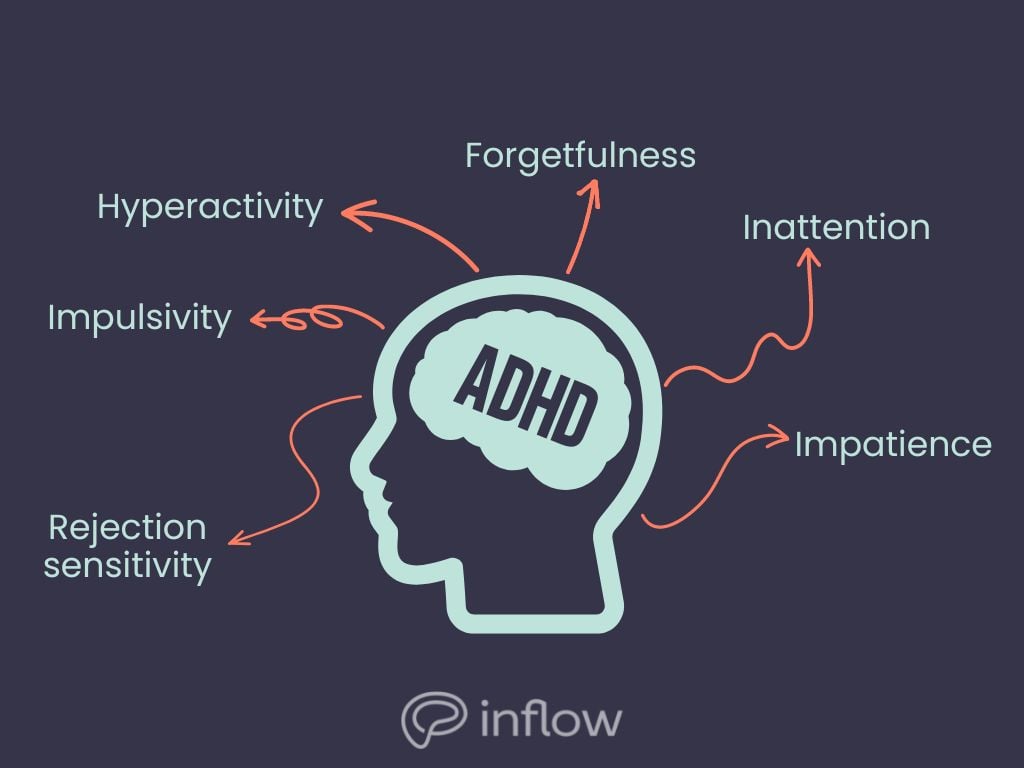
Common symptoms of ADHD
ADHDers usually experience the following symptoms, among others:
- Difficulty concentrating
- Impulsivity
- Hyperactivity
- Rejection sensitivity
- Distractibility
- Forgetfulness
Is there a cure for ADHD?
While there’s no ‘cure’ for ADHD, several therapeutic techniques and medications can help manage symptoms.
ADHD medications:
- Adderall
- Concerta
- Vyvanse
- Ritalin
- Focalin
- Wellbutrin
- Strattera
Therapy
In addition to prescription medications, certain behavioral therapies—cognitive behavioral therapy, or CBT—can treat ADHD, with or without medication.
So, how are ADHD symptoms affected by pregnancy?
ADHD and pregnancy
Unfortunately, there are few studies that examine neurological effects of ADHDers during pregnancy and postpartum. This is mostly due to FDA regulations regarding the inclusion of pregnant women in research studies.1
Surprisingly, women with ADHD frequently report decreased severity of ADHD symptoms while pregnant. Some even say their symptoms disappear completely—temporarily, of course.
But… why?
Estrogen and ADHD
All humans—men, women, and intersex individuals—produce estrogen, unless they have a condition causing estrogen deficiency.2,3
Estrogen heavily influences dopaminergic pathways in the brain,4 which transport dopamine—a key neurotransmitter involved in cognitive and executive functioning.
During pregnancy, the body naturally increases estrogen levels, so the hormone is always present in the bloodstream. However, ADHD symptoms typically return after delivery due to the rapid decline of estrogen.
Risks
Aside from hormonal changes, pregnant ADHDers—and their womb nuggets—may be at a higher risk of complications5, regardless of medication history:
ADHD mothers and their pregnancies:
- Preeclampsia
- Emergency cesarean delivery
- Preterm labor and delivery
Babies of ADHD mothers
- Breathing difficulties during and after delivery
- Emergency newborn resuscitation
- Neonatal admission
Are ADHD medications safe for pregnancy?

Many people diagnosed with ADHD take stimulants or nonstimulants to manage their symptoms. But - are they safe to use while pregnant? If so, which ones?
Unfortunately, with the exclusion of pregnant people in research studies, it’s hard to give a definitive answer.
Psychostimulant medications
Some stimulant medications are associated with risks that can adversely affect fetal development, delivery, and survival.6 Because of this, many mothers discontinue their prescription stimulants until after delivery.
However, it’s also possible that a sudden discontinuation of a stimulant regimen during pregnancy—or any time—may cause severe depression and withdrawal symptoms.7
To continue or discontinue medications...?
For expectant mothers who can’t decide if they should continue taking ADHD medication during pregnancy, they should first speak with their general practitioner and obstetrician/midwife to determine if the benefits outweigh the risks.
In addition, they should ask themselves the following questions6 to gauge the risks of discontinuation:
- How have I functioned in the past at work or school without medication?
- How is my driving without ADHD medication? Do I have a history of causing accidents?*
*for those with drivers’ licenses
Nonstimulant medications
Generally, nonstimulants are ‘safe’ for pregnant ADHDers. In fact, many ADHD mothers with stimulant prescriptions temporarily switch to a nonstimulant regimen during their pregnancy.
As always, though, it’s important to discuss your situation with your healthcare providers to determine what’s best for you and your baby.
Is it safe to take stimulant medications while breastfeeding?
Consuming large doses of ADHD stimulants may affect breast milk. While low doses of stimulants are typically harmless to nursing infants, larger quantities may pose a risk to milk production.
Extended release vs. immediate release
Immediate release versions of amphetamine-based stimulants are a better option for nursing mothers compared to extended-release. This has to do with the timing of the concentration peak—and following decline—of amphetamines in the blood after consumption.8
Other ADHD treatment options for expectant mothers (no medication required!)

There are several ADHD treatment routes that don’t involve medication. Below are tips and strategies for ADHD mamas looking for symptom relief—without using drugs like Adderall, Strattera, or Vyvanse.
Get plenty of sleep
It’s recommended that everyone gets at least seven hours of sleep each night, but this is especially true for expectant moms.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
This form of behavioral therapy can ease feelings of anxiety, and help with sorting through anxious thoughts and feelings about becoming a parent.9
ADHD support groups, communities, and apps
A group of people experiencing similar situations can provide support and advice to make the pregnancy journey smoother. Find your place in an online community—like ADHD Twitter—or try ADHD management apps, such as Inflow.
Exercise
Low-impact exercise—walking, yoga, swimming—aid pregnant mothers in managing ADHD while keeping them active. (Be sure to check with your doctor on this one!)
Frequently asked questions
Does pregnancy make ADHD worse?
Yes and no. High estrogen levels are linked with increased dopamine production and transportation efficiency.4 During pregnancy, estrogen levels drastically increase, which increases dopamine. For most pregnant people, this reduces the severity of ADHD symptoms.
But! After delivery, hormonal levels typically return to normal; and that sudden depletion of estrogen can cause depression as well as worsened — or a return of — ADHD symptoms.
Is ADHD worse after pregnancy?
Again — yes and no. It depends on what you’re comparing your postpartum ADHD symptoms to... ADHD symptoms during pregnancy, or ADHD symptoms before pregnancy.
Is ADHD worse after pregnancy, compared to during pregnancy? Typically, yes. This is caused by the drop in estrogen levels.
Is ADHD worse after pregnancy, compared to before pregnancy? Typically, no, but there are exceptions. For example, women suffering from postpartum depression (PPD); or those who experienced miscarriage, stillbirth, or a traumatic birth may notice worse ADHD symptoms after pregnancy.
What can I take instead of Adderall while I’m pregnant?
Discontinuation of any medication should be discussed with your healthcare provider. For pregnant ADHDers, you’ll want to weigh the risks and benefits of discontinuing stimulants.
If you decide that discontinuation is right for you, it’s possible to treat ADHD with nonstimulant medications while pregnant. Additionally, lifestyle changes can help with symptom management, as well as supportive communities and other resources.
Does caffeine during pregnancy cause ADHD?
There is no evidence that a mother's caffeine consumption can cause the development of ADHD in a fetus.
Can Adderall hurt a fetus?
There is scientific evidence that stimulant medications (Vyvanse, Adderall, Ritalin, Concerta, Focalin, etc.) increase the risk of pregnancy and birth complications, such as preterm delivery, neonatal admission, and preeclampsia.6
However, the benefits of continuing your regimen may outweigh those risks.7 Discuss this with your doctor before deciding.
-
Sources
1 U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Pregnant Women: Scientific and Ethical Considerations for Inclusion in Clinical Trials - Guidance for Industry
2 Biology of Reproduction | Estrogen in the male: a historical perspective
3 Osteoporosis and the Osteoporosis of Rheumatic Diseases | Estrogen Deficiency
4 International Journal of Molecular Sciences | The Role of Estrogen Receptors and Their Signaling across Psychiatric Disorders
5 CNS Drugs | Perinatal Outcomes of Women Diagnosed with Attention-Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder: An Australian Population-Based Cohort Study
6 The American Journal of Psychiatry (AJP) | ADHD and Pregnancy
7 Brain Communications | Dependence, withdrawal and rebound of CNS drugs: an update and regulatory considerations for new drugs development
8 Pharmaceutical Research | Pharmacological Treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder During Pregnancy and Lactation
9 Brazilian Journal of Psychiatry (BJP) | Cognitive-behavioral therapy in pregnant women with generalized anxiety disorder: a retrospective cohort study on therapeutic efficacy, gestational age and birth weight

.png)



.jpg)
